Interferential

Combination
Back Overview and description of the therapeutic applications
1. Sub-acute per arthritis humero-scapularisI Interferential (2-pole; AMF 100 HZ; spectrum 100 hz spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time :15 minutesSuggested advice : intensity pleasantly noticeable
Treatment frequency : 5x per week.
2 Chronic lumbago
Interferential (2-pole); AMF 10 Hz; spectrum 90 hz spectrum time 6 s; Contour 100%
Treatment time : 10 minutes
Suggested advice : intensity strongly noticeable.
Treatment frequency ; 3x per week
3 Arthrosis
Interferential (2- pole); AMF 50 Hz, spectrum 50 Hz spectrum time 6s; contour 1 %)
Treatment time; 12 minutes
suggested advice; intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency; 3x per week.
4 Contractures after immobilization
Interferential (2- pole); AMF 2 Hz, spectrum 10 Hz spectrum time 6s; contour 100 %)
Treatment time; 15 minutes
suggested advice; intensity to be increased until rhythmic contraction occur
Treatment frequency; daily
5 Post-operative pain
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time ; 15 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
6 Neuralgia
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 75 hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time ; 20 minutes.
Suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
7 Herpes zoster
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 75 hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time ; 10 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
8 Epicondylitis humeri lateralis- manifesting radiation in extensors
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 200 ms; pulse frequency 80 hz;spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 100%
Treatment time ; 10 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
9 Actual segmental disarticulations
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 80 ms; pulse frequency 50 hz; spectrum 100 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 100%
Treatment time ; 25 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable/ pleasant tingling sensation
Treatment frequency; 5 x per week
10 Tension headache
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 100 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; burst frequency 2 hz)
Treatment time ; 15 minutes
suggested advice : intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency; 3 x per week
11 Circulation-disorders - calf- muscles
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 200 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; burst frequency 2 hz)
Treatment time ; 15 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency; 3 x per week
12 Acute muscle rupture
Ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2; 1 MHZ; duty-cycle 1:4;intensity 0.8 w/cm2
Treatment time : 7 minutes .
Suggested advice: intensity just noticeable
Treatment frequency; 3x per week.
13 Epicondylitis laterals - low actually
Ultrasound therapy ( treatment head 4 cm2; 1 MHZ; duty-cycle 1:1;intensity 0.4 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 7 minutes.
suggested advice: intensity just noticeable.
treatment frequency :3x per week.
14 Injury medical collateral ligament art. Genus
Ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2; 1 MHz; duty-cycle 1:4 ;intensity 1.5 W/cm2)
intensity time :20 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency : 3x per week
15 Detection of pain-points
Combination therapy: interferential (AMF 100 Hz; spectrum 0hz)and Ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 , 1 MHZ;duty-cycle 1;1 intensity 1.0 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 20minutes
Treatment advice: intensity well noticeable. The treatment time depends on the size of the body area to be treated.
16 chronic lumbago
Interferential (2-pole); AMF 10 Hz; spectrum 90 hz spectrum time 6 s; Contour 100%
Treatment time : 10 minutes
Suggested advice : intensity strongly noticeable.
Treatment frequency ; 3x per week
17 Gonarthrosis
Combination therapy: interferential (AMF 100 Hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 1%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 1 MHZ; duty-cycle 1;4; intensity 0.5 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 7 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency: 3x per week
18 Chronic distortion pedis
combination therapy: tens continuous (pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; contour 1%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4cm2, ! MHz; duty-cycle 1:4; intensity 0.5 W/cm2
Treatment time :7 minutes.
Suggested advice: Intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency: 3x per week
19 Ischialgy
combination therapy; tens continuous (pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; contour100%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 1 MHz; duty-cycle 1:1; intensity 0.5 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 10 minutes
suggested advice: Intensity noticeable
treatment Frequency; daily
20 Acute subluxation humeri
Combination therapy; tens continuous (pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; contour100%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 1 MHz; duty-cycle 1:1;intensity 1.0 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 5 minutes
suggested advice: Intensity just noticeable
treatment Frequency; daily
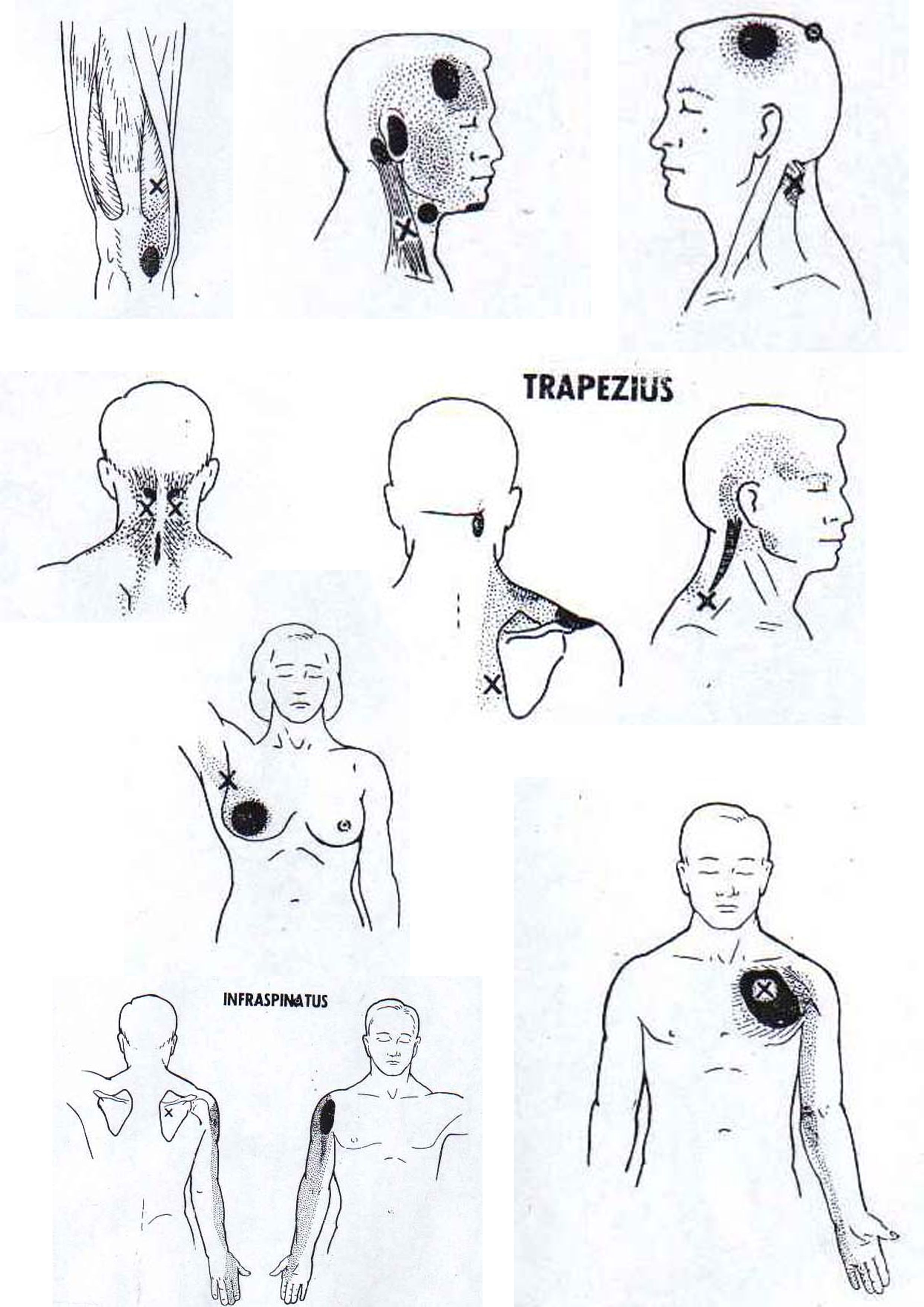
Ultrasonic

Triggerpoint
Physiotherapy staffing
Staffing of Physiotherapy Department
PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGER OR DIRECTOR.is
SENIOR PHYSIOTHERAPIST (To supervise basic P. T & reports to Manager). PHYSIOTHERAPIST (To supervise physiotherapy assistant maintenance of record). PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSISTANT.(To supervise helper& Pt. Communication feedback to Physiotherapist).
HELPERS (Pt. Communication feed back to Physiotherapist).
UP GRADATION OF PHYSIOTHERAPY
Once pt. Is being admitted in the hospital it means his physical condition deteriorated day by day. So every pat. Before discharge from the hospital must have physiotherapy advice including home exercise prong. Once pat. Is being referred in Physiotherapy department he must be evaluated documented properly purely in professional manner than treated, progress, follow up and record must be maintained.
Physiotherapy does not mean simply exercises and operation of machine that can be done by Physiotherapy assistant, they are especially trained in various exercises and operation of machines, they must work under supervision of qualified Physiotherapist trained in various specialty.
Qualified Physiotherapist means to advice, explain patient problem, disability to discuss physical complication related to patients medical hindrance, to evaluate patient physical disability to monitor progress.
INVOLVEMENT OF PHYSIOTHERAPIST
Evaluate patient professionally.
Plan & implement physiotherapy treatment.
Provide home exercise program.
Monitor progress of pat.
Supervise & educate Physiotherapy Assistant.
PHYSIOTHERAPY INVOLVEMENT WITH HOSPITAL STAFF
To arrange courses for Nursing staff.
Lifting & transfer pat. Which makes nursing staff affective with minimal Physical strain to their body.
To organize various ergonomically meetings with various staff to make hospital staff members less Physically strained.
Monitor progress of pat.
Supervise & educate Physiotherapy Assistant.
DUTIES OF SENIOR PHYSIOTHERAPIST
To arrange meetings with patients family if needed to educate physical disability, documents and maintain record meetings.
Provide guidelines to basic Physiotherapist in their respective fields. Rotate physiotherapist monthly in various field.
Provide unto update knowledge about know how in the world of physiotherapy by the help of Internet.
Maintain discipline in the dept.
Maintain standard & behavior with staff and patient.
Solve various complains related to staff, Patient and physiotherapy Assistant.
To monitor and supervise relations of patients those who are not satisfied with the treatment.
DUTIES OF PHYSIOTHERAPY DIRECTOR/MANAGER
Look after welfare of organization.
Submit reports of Physiotherapy department monthly.
Maintain relation with various consultants.
Answerable to various consultants.
Look after hazards in departments & discuss with legal advisor .Upgrade standard.
Concentrate marketing of Physiotherapy departments.
To improve economy of department.
Discuss departmental problems with Senior Physiotherapist.
Supervise planning of Physiotherapy departments.
To upgrade unto International standard & concentrate on International market.
TO UPGRADE PHYSIOTHERAPY IN THE FIELD OF
Psychiatry
Gynecological conditions
Geriatric conditions
Burns
Urology
Wheel chair and ADL standard
Ergonomically evaluation of various companies senior executives to decrease physical strain.
Exercise
Flexion
Extension
Sideward flexion (Rt. /Lt.) Sideward flexion (Rt./Lt.)
Sideward rotation (Rt./Lt.)
Sideward Rotation (Rt./Lt.)
Hip
To mobilise the hip, to strengthen the muscle and particularly the muscles of the buttocks, to stretch the loin iliac muscle and the adductor muscles.
How to carry out the exercises : Preferable on a hard surface.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Lying on the back

Starting Position
Lying on the back with legs stretched out.
Method :
Without lifting the left leg from the floor, bend the right leg and bring it over the chest. Return to starting position and repeat the same movement with the left leg.
Spinal
Objectives
To mobilise the spinal segment and to correct the postural distortion,to strengthen the extensor muscles
of the back and the muscles of the shoulder blades and to develop the pectoral muscles.
How to do it : Always, if possible, on a hard surface, with a thin carpet.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Lying on back, face upwards

Starting Position
Lying on back, legs drawn up, knees bent, feet touching floor, arms alongside body.
Method :
(i) Breathe in, raising both arms, stretching them beyond the head on the floor.
(ii) Bring arms down extending them sideways to the floor at shoulder level while breathing out, then revert to starting position.
After several sessions, the exercise should be performed with a weight of 0.5-1.0 kg. in each hand.
Lumbar
Objectives
To mobilize the lumber spinal column and the coccyco-vertebral articulation. To strengthen the abdominal and glutei muscles.
To correct the lumber surface
To be carried out : Preferably on a hard surface.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Lying on the side

Starting Position
Lying down on the right side with right hand bent at elbow and tucked under head, left hand resting on floor, palm downwards in
line with the chest, left leg stretched out with toes touching floor. Right leg flexed and tucked under.
Method :
(i) Raising the left leg, draw the knee towards the chest, curving the lumbar region.
(ii) Extend the leg backwards, while raising the lumbar spine. Repeat exercise by turning on the other side.
Shoulder
To mobilize the shoulder(front raising, bending backwards raising sideward's, rotating it inwards and outwards). To extend the muscles which form the front and rear walls of the armpits. To relax and strengthen the shoulder girdle as also the arm muscles.
How to carry out the exercises : To carry out the exercises with both the arms simultaneously with the exception of those which are to be carried out with them being laid on the sides.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Standing
Exercise 1
Starting Position
Standing firmly, with truck bent forwards, and both arms hanging loose
Swing the arms forwards and backwards vigorously several times.
moreElbow
To mobilize the elbow (flexing, extending, bending forwards as well as bending backwards). To strengthen the bending and extending muscles of the arm.
How to carry out the exercises : In the same way as in the exercises of the shoulder which are performed in the sitting position, the arms must rest upon a hard surface. One has to take care to see that the movements are not made difficult by the clothes.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Lying on back, face upwards Exercise : Lying on back, face upwards
Exercise 1
Starting Position
Lying on back, with arms outstretched on either side at shoulder level.
Flexion and extension of the forearms. Subsequently this exercise must be done with weights up to 2 kg's. in each hand.
moreTo mobilize the wrist and the fingers to stretch and to strengthen the musculature of the forearm.
How to carry out the exercises : The Exercises Shall be performed simultaneously withes bother the hands, taking Care to see that the move aments are not made difficult by the clothes.
Exercise A : Seated at table with forearms and hands resting on it.
Exercise 1
Starting Position
Sitting with forearms and hands resting on a table.
Raise the hands without moving forearms.
moreKnee
To mobilize the knee, to strengthen the quadriceps and to strengthen the is chiocrural muscles.
How to carry out the exercises : The exercises shall be performed preferably on a hard surface. Take care to see that the legs are not obstructed in their movements by clothing.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Lying on the back
Exercise 1
Starting Position
Lying on the back with both legs stretched out straight.
Pressing the knee down firmly on the floor, pull the toes in towards the body. In the beginning it is advisable to do the exercise with both legs simultaneously.
moreTo mobilize the joints of the ankles and the joints of the toes of the feet, and to strengthen the muscles of the legs and the feet.
How to carry out the exercises : One must take care to see that the movements of the feet are not made difficult by the clothes. In the beginning, the exercises shall be performed only in sitting position, following which, the exercises of the position of the feet shall be added. One must make both the feet work together.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Seated upon a bed or the floor
Exercise 1
Starting Position
Seated with legs stretched out in front.
Pull the toes inwards towards the body, then bend them down to the maximum extent possible.
moreCervical
To mobilize the cervical segment and to correct its defective condition and to relax the muscles of the neck and muscles of the shoulder girdle.
How to carry out the exercises : Before a mirror, if possible, in order to check and correct oneself.
Note : Please Do all the movements as slow as possible....!
Exercise : Seated at table with forearms and hands resting on it.
Exercise 1
Starting Position
Sit up straight on a stool, feet together, arms on the side keeping the mouth closed.
Bend the head and let it fall forwards till the chin touches the chest, and then slowly bend the head back as far as it goes.
more