Interferential

Combination
Back Overview and description of the therapeutic applications
1. Sub-acute per arthritis humero-scapularisI Interferential (2-pole; AMF 100 HZ; spectrum 100 hz spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time :15 minutesSuggested advice : intensity pleasantly noticeable
Treatment frequency : 5x per week.
2 Chronic lumbago
Interferential (2-pole); AMF 10 Hz; spectrum 90 hz spectrum time 6 s; Contour 100%
Treatment time : 10 minutes
Suggested advice : intensity strongly noticeable.
Treatment frequency ; 3x per week
3 Arthrosis
Interferential (2- pole); AMF 50 Hz, spectrum 50 Hz spectrum time 6s; contour 1 %)
Treatment time; 12 minutes
suggested advice; intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency; 3x per week.
4 Contractures after immobilization
Interferential (2- pole); AMF 2 Hz, spectrum 10 Hz spectrum time 6s; contour 100 %)
Treatment time; 15 minutes
suggested advice; intensity to be increased until rhythmic contraction occur
Treatment frequency; daily
5 Post-operative pain
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time ; 15 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
6 Neuralgia
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 75 hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time ; 20 minutes.
Suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
7 Herpes zoster
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 75 hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 50%
Treatment time ; 10 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
8 Epicondylitis humeri lateralis- manifesting radiation in extensors
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 200 ms; pulse frequency 80 hz;spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 100%
Treatment time ; 10 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency; daily
9 Actual segmental disarticulations
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 80 ms; pulse frequency 50 hz; spectrum 100 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 100%
Treatment time ; 25 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable/ pleasant tingling sensation
Treatment frequency; 5 x per week
10 Tension headache
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 100 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; burst frequency 2 hz)
Treatment time ; 15 minutes
suggested advice : intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency; 3 x per week
11 Circulation-disorders - calf- muscles
Tens continuous (Pulse duration 200 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; burst frequency 2 hz)
Treatment time ; 15 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency; 3 x per week
12 Acute muscle rupture
Ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2; 1 MHZ; duty-cycle 1:4;intensity 0.8 w/cm2
Treatment time : 7 minutes .
Suggested advice: intensity just noticeable
Treatment frequency; 3x per week.
13 Epicondylitis laterals - low actually
Ultrasound therapy ( treatment head 4 cm2; 1 MHZ; duty-cycle 1:1;intensity 0.4 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 7 minutes.
suggested advice: intensity just noticeable.
treatment frequency :3x per week.
14 Injury medical collateral ligament art. Genus
Ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2; 1 MHz; duty-cycle 1:4 ;intensity 1.5 W/cm2)
intensity time :20 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity just noticeable.
Treatment frequency : 3x per week
15 Detection of pain-points
Combination therapy: interferential (AMF 100 Hz; spectrum 0hz)and Ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 , 1 MHZ;duty-cycle 1;1 intensity 1.0 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 20minutes
Treatment advice: intensity well noticeable. The treatment time depends on the size of the body area to be treated.
16 chronic lumbago
Interferential (2-pole); AMF 10 Hz; spectrum 90 hz spectrum time 6 s; Contour 100%
Treatment time : 10 minutes
Suggested advice : intensity strongly noticeable.
Treatment frequency ; 3x per week
17 Gonarthrosis
Combination therapy: interferential (AMF 100 Hz; spectrum 50 hz; spectrum time 6 s; contour 1%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 1 MHZ; duty-cycle 1;4; intensity 0.5 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 7 minutes.
suggested advice : intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency: 3x per week
18 Chronic distortion pedis
combination therapy: tens continuous (pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; contour 1%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4cm2, ! MHz; duty-cycle 1:4; intensity 0.5 W/cm2
Treatment time :7 minutes.
Suggested advice: Intensity well noticeable.
Treatment frequency: 3x per week
19 Ischialgy
combination therapy; tens continuous (pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; contour100%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 1 MHz; duty-cycle 1:1; intensity 0.5 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 10 minutes
suggested advice: Intensity noticeable
treatment Frequency; daily
20 Acute subluxation humeri
Combination therapy; tens continuous (pulse duration 50 ms; pulse frequency 100 hz; contour100%) and ultrasound therapy (treatment head 4 cm2 1 MHz; duty-cycle 1:1;intensity 1.0 W/cm2)
Treatment time : 5 minutes
suggested advice: Intensity just noticeable
treatment Frequency; daily
Ultrasonic

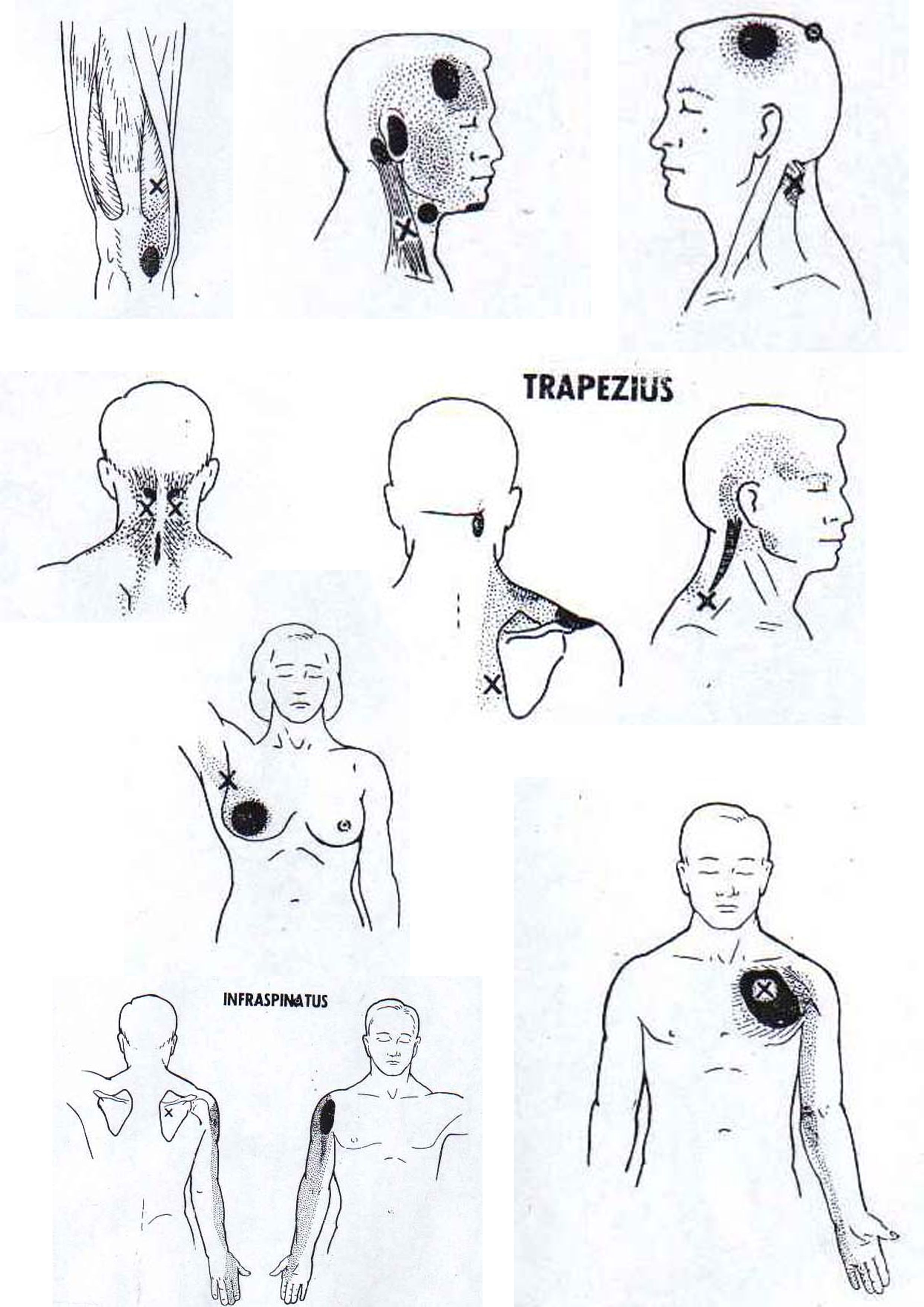
Triggerpoint
Physiotherapy staffing
Staffing of Physiotherapy Department
PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGER OR DIRECTOR.is
SENIOR PHYSIOTHERAPIST (To supervise basic P. T & reports to Manager). PHYSIOTHERAPIST (To supervise physiotherapy assistant maintenance of record). PHYSIOTHERAPY ASSISTANT.(To supervise helper& Pt. Communication feedback to Physiotherapist).
HELPERS (Pt. Communication feed back to Physiotherapist).
UP GRADATION OF PHYSIOTHERAPY
Once pt. Is being admitted in the hospital it means his physical condition deteriorated day by day. So every pat. Before discharge from the hospital must have physiotherapy advice including home exercise prong. Once pat. Is being referred in Physiotherapy department he must be evaluated documented properly purely in professional manner than treated, progress, follow up and record must be maintained.
Physiotherapy does not mean simply exercises and operation of machine that can be done by Physiotherapy assistant, they are especially trained in various exercises and operation of machines, they must work under supervision of qualified Physiotherapist trained in various specialty.
Qualified Physiotherapist means to advice, explain patient problem, disability to discuss physical complication related to patients medical hindrance, to evaluate patient physical disability to monitor progress.
INVOLVEMENT OF PHYSIOTHERAPIST
Evaluate patient professionally.
Plan & implement physiotherapy treatment.
Provide home exercise program.
Monitor progress of pat.
Supervise & educate Physiotherapy Assistant.
PHYSIOTHERAPY INVOLVEMENT WITH HOSPITAL STAFF
To arrange courses for Nursing staff.
Lifting & transfer pat. Which makes nursing staff affective with minimal Physical strain to their body.
To organize various ergonomically meetings with various staff to make hospital staff members less Physically strained.
Monitor progress of pat.
Supervise & educate Physiotherapy Assistant.
DUTIES OF SENIOR PHYSIOTHERAPIST
To arrange meetings with patients family if needed to educate physical disability, documents and maintain record meetings.
Provide guidelines to basic Physiotherapist in their respective fields. Rotate physiotherapist monthly in various field.
Provide unto update knowledge about know how in the world of physiotherapy by the help of Internet.
Maintain discipline in the dept.
Maintain standard & behavior with staff and patient.
Solve various complains related to staff, Patient and physiotherapy Assistant.
To monitor and supervise relations of patients those who are not satisfied with the treatment.
DUTIES OF PHYSIOTHERAPY DIRECTOR/MANAGER
Look after welfare of organization.
Submit reports of Physiotherapy department monthly.
Maintain relation with various consultants.
Answerable to various consultants.
Look after hazards in departments & discuss with legal advisor .Upgrade standard.
Concentrate marketing of Physiotherapy departments.
To improve economy of department.
Discuss departmental problems with Senior Physiotherapist.
Supervise planning of Physiotherapy departments.
To upgrade unto International standard & concentrate on International market.
TO UPGRADE PHYSIOTHERAPY IN THE FIELD OF
Psychiatry
Gynecological conditions
Geriatric conditions
Burns
Urology
Wheel chair and ADL standard
Ergonomically evaluation of various companies senior executives to decrease physical strain.
Pelvic Exercise
Pelvic Floor Exercises and Stress Incontinence
Purpose of Floor Exercises :
The purpose of pelvic floor exercises is to re-educate the pelvic floor muscles so that they are able to control the flow of urine more efficiently. It should be emphasized that pelvic floor exercises are only designed to help people with genuine stress incontinence caused and are not appropriate for the management of incontinence caused by many other factors.
This article describes a series of exercises which you need to carry out several times a day for at least six months as it will take time for your muscles to adjust. Your doctor or nurse, should be able to help you if you experience any difficulty or if there is anything you do not understand.
The urethra, or outlet tube which carries urine from the bladder to outside your body, passes, through a set of muscles called the pelvic floor muscles. These enable the urethra to close and prevent urine from escaping.
If these muscles become flabby and unable to contract efficiently urine may escape from the uretha involuntarily when extra pressure is put on the bladder, especially during moments, of exertion such as when lifting, bending, jumping, coughing, sneezing or laughing. This condition is called stress incontinence.
In women, lack of tone in the pelvic muscles may result from a period in which the pelvic floor muscles were relatively inactive, such as following chidbirth or pelvic surgery. In men the condition may occur following a prostatectomy or bladder surgery. In both, stress incontinence may also be due to bad postural habits which are often associated with overweight.
How to begin
First of all, try practicing stopping and starting the flow of urine when you need to go to the toilet. To start with try doing this once towards the end of the stream and gradually work up to starting the flow of urine when you need to go to the toilet. To start with try doing this once towards the end of the end of the stream and gradually work up to starting and stopping three to four times and near the beginning of the stream as well. Do this until you feel confident that you have immediate control of the flow.
What to do next
Sit well back on a hard chair, thighs and feet supported, legs well apart. Lean forward with your elbows on your knees and your head dropped . Consciously relax your stomach and buttock muscles. Then follow the exercises below

Exercise the muscles around your back passage by pretending that you are trying to stop a burst of diarrhea ar wind while you count slowly up to four. Then let go. Try to let go even more and then tighten as hard as you can. Hold and relax until you are confident doing this exercise.
Now exercise the muscles around your front passage by pulling up the muscles as hard as you can taking care not to tighten your stomach or buttock muscles. This is the same as the exercise you practiced first when you tried to stop the flow of urine in mid stream. Hold the muscle up as hard as you can while you count to four, then consciously relax it. Repeat the exercise until you feel confident you are fully in control.
The next thing is to try and combine both exercises, tightening both sets of muscles simultaneously as hard as you can, holding to the count of four, and then relaxing. Repeat this about five times. When you can tighten both sets of muscles, front and back, try to pull up hard on the middle area, to get a lift from front to back. Again hold and relax about five times.
Finally try pulling up an all three areas simultaneously and hold for a count of four. Repeat this about five times.
Once you have mastered all the exercises you no longer need to do them separately, and can practice them anywhere at anytime, and in a variety of positions. The exercises should be repeated four times and done ten times a day.
may find the following advice helpfullyTry setting aside a regular time to do your exercises each day. You should perform them about eight times at lease twice aday. Start your exercise routine gently and gradually increase the length of time and severity of exercise over a period of time. Perform your exercise at a time and place convenient to you; they can be done when you go to the toilet but also at other times, eg. when you are brushing your teeth. You may find that adopting a different position from the basic chair sitting one is easier for you.
Lying in bed, on back or side, with knees crooked

Lying position for pelvic floor exercises
Standing, leaning forwards from the hips with hands flat on the table.

Standing Position for Pelvic floor exercises.
Kneeling on all fours.
Every now and again check in a mirror when you are doing the exercises that you are not moving the muscles in your stomach, buttocks or thighs. You should not be able to see the muscles moving at all. It would be a waste of time and effort if you spent several weeks exercising the wrong muscles!
If you are not sure whether you are using the correct muscles, your continence advisor may be able to lend you an electronic stimulator. This is a painless way of helping you to exercise the correct muscles.
Women may also find weighted vaginal cones helpful. The plastic cones are about 5cm long and have a string attached to the narrow end. They are available from pharmacists or through continence advisors in sets of five with gradually increasing weight, 10 to 100g. The idea is to start with the lightest cone and to build up to the heaviest over several months. The cone is inserted into the, vagina with the string downwards and is then held in place by contracting the pelvic floor muscles. The cone is left in place for 10-15 minutes while you wash up or cook example. This is repeated 3-4 times a day.
Exercises that help tone up the muscles such as those used for slimming can also be beneficial especially for women after childbirth. Swimming is a general exercise that can help improve pelvic muscle floor tone.
